India is a historical and culturally rich country that has produced many architectural wonders. Heritage homes are among them; they are mute witnesses to centuries of custom, development, and the diverse fabric of Indian life. These houses provide an intriguing window into the past since they are frequently embellished with elaborate carvings, elaborate decorations, and distinctive architectural styles. Let’s examine the background, design, and current restoration projects of these recognizable buildings.
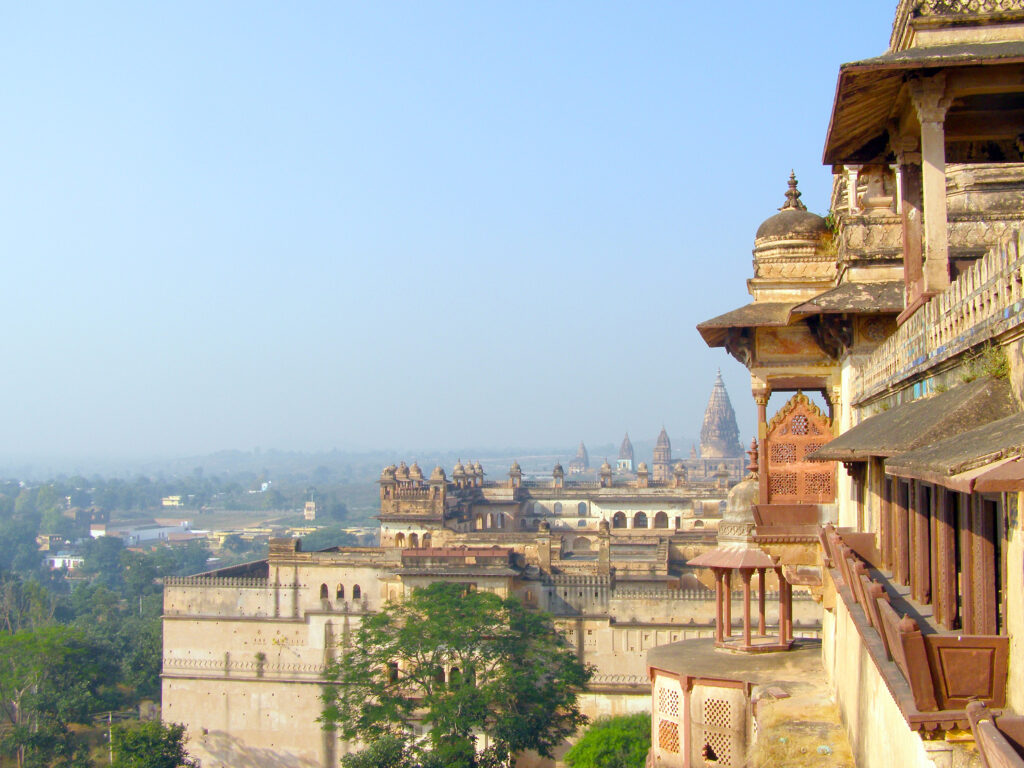

An Overview of India’s Heritage Houses’ History
In India, heritage homes have a long history that begins in antiquity. These homes, which range from the opulent palaces of kings and emperors to the humble homes of commoners, have greatly influenced the social, cultural, and economic makeup of Indian culture. These houses’ architectural styles are a result of a variety of influences, such as foreign invasions, religious doctrine, and local customs.
➡️Vedic Period: Mud and wood dwellings that are basic and practical.
➡️Mauryan Empire: Greek and Persian architectural designs led to more ornate dwellings.
➡️Gupta empire: The Ajanta, Ellora, and Badami caves are prime examples of the Gupta Empire’s architectural splendor.
➡️India throughout the Middle Ages: A fusion of Islamic and Indian architectural forms produced amazing buildings like the Red Fort and Taj Mahal.
➡️Colonial India: Colonial bungalows and mansions in India were made possible by the introduction of European architectural styles.
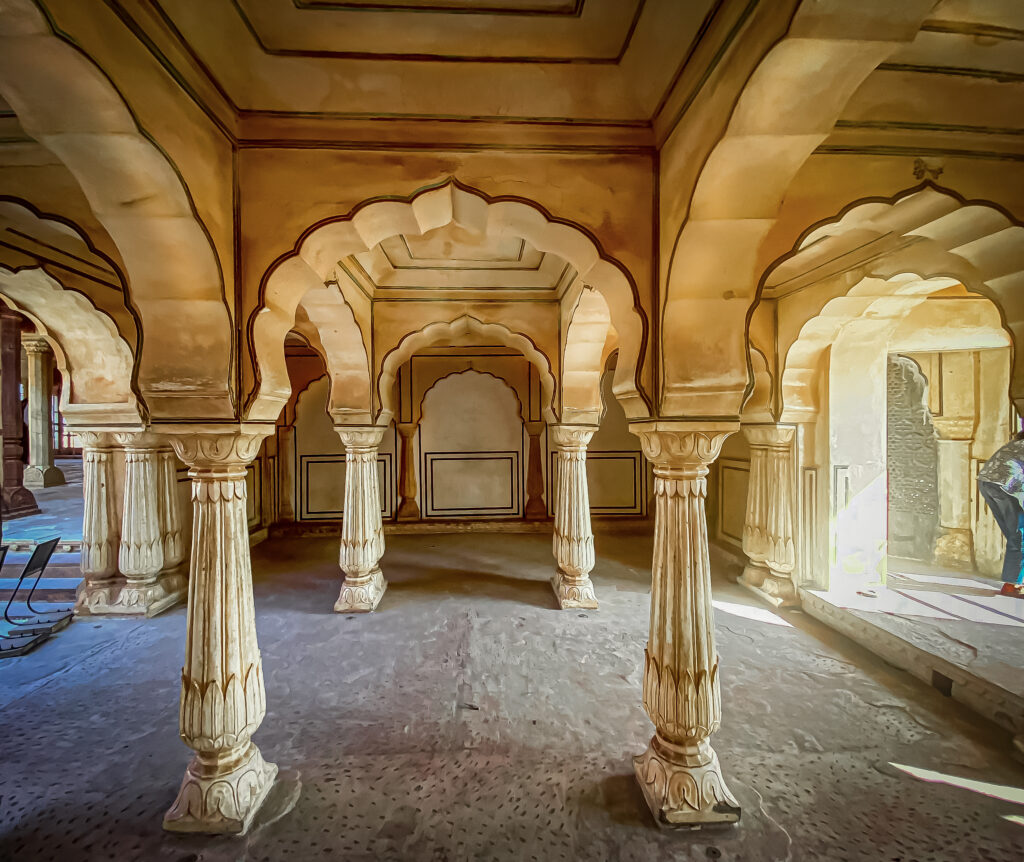

The Importance of Restoring Historic Homes
Heritage dwellings must be preserved for a number of reasons.
➡️Cultural Heritage: They serve as priceless archives of Indian history.
➡️Architectural Significance: They display distinctive designs and methods.
➡️Potential for Tourism: They can draw visitors and strengthen regional economies.
India’s Restoration Initiatives
The value of restoring historic homes has come to light more and more in recent times. To protect and restore these historic properties, a number of efforts have been launched by NGOs, government organizations, and private citizens. But problems including a lack of resources, knowledge, and legal barriers still exist.
The Ancient Monuments Preservation Act of 1904 and the Ancient Monument and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act of 1958 assign the Archaeological Survey of India, which was founded in 1861, the duty of safeguarding and preserving 3679 monuments and archaeological sites deemed to be of national significance.
Neolithic sites, megalithic graves, megalithic rock shelters, rock-cut caves, stupas, temples, churches, synagogues, mosques, tombs, palaces, forts, bathing Ghats, water reservoirs, tanks, bridges, pillars, inscriptions, kos minars, diggers’ sites, and more are among the rich variety of built heritage that the Archaeological Survey of India conserves and preserves.
One of the Archaeological Survey of India’s main responsibilities is the maintenance, conservation, protection, and environmental development of the 3679 centrally protected monuments and sites. This work is done after an annual conservation program is prepared.
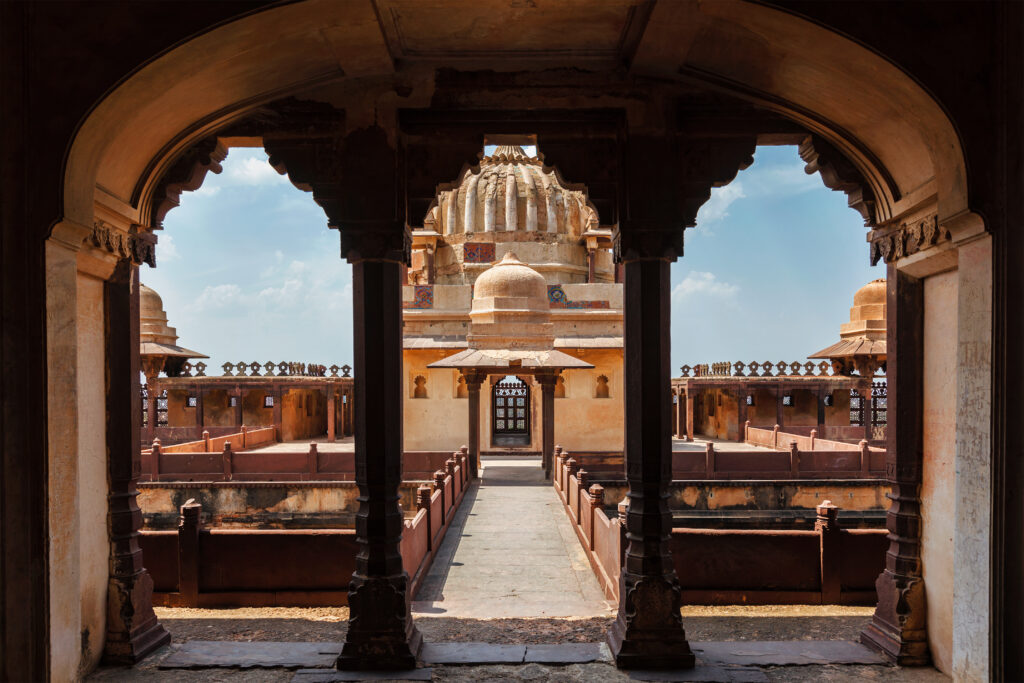

Heritage Houses’ Architectural Styles
India’s heritage houses exhibit a wide variety of architectural designs, each of which captures the distinct historical and cultural background of its locale. The following are a few of the most popular styles:
The Architecture of Indo-Islam
➡️Important features include: large scale, detailed carvings, the use of domes and arches, and the blending of Islamic and Indian elements.
➡️Example: Red Fort, Jama Masjid, and Taj Mahal
➡️Mughal, Central Asian, and Persian architectural traditions are among the influences.
➡️Large courtyards, elaborate decorations, minarets, and symmetrical layouts are some of the distinctive features.
Colonial Style Buildings
➡️Important features include the use of brick and stone, symmetry, classical proportions, and European styles—especially British.
➡️Mansions, government buildings, and colonial bungalows are a few examples.
➡️Gothic, Baroque, and Neoclassical styles are among the influences.
➡️Pitch roofs, Corinthian columns, and Palladian windows are characteristic features.
Authentic Architecture
➡️Important attributes: based on regional needs and lifestyles, rooted in customs and materials.
➡️Examples include communal buildings, temples, and traditional homes.
➡️Influences include the local environment, the accessibility of materials, and cultural customs.
➡️Use of regional materials like thatch, bamboo, and mud, as well as original architectural designs and layouts, are characteristic features.
Additional Notable Designs
➡️South India’s Dravidian architecture is distinguished by its elaborate carvings, mandapas (halls), and gopurams (tower entrances).
➡️Nagara architecture is found in North India and is distinguished by elaborate sculptures, mandapas, and shikharas, or conical spires.
➡️Central India’s Vesara architecture is a fusion of Nagara and Dravidian design elements.
Conclusion :
India’s heritage residences are priceless reminders of the nation’s rich past and cultural legacy. By protecting these landmark assets, we add to the rich fabric of India’s past, present, and future in addition to protecting our cultural legacy. With the help of government programs, non-governmental organizations, and private citizens, we can guarantee that these historic houses will be preserved and treasured for many more generations. Together, let’s embrace our architectural heritage and make sure it is preserved for future generations.
Source: All Rights and Credit reserved to the respective owners





Top Northern Indian Cities Where Land Value Is Set to Surge in the Next 3 Years